 On July 4th, 2015, draft amendments to Canada’s Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Regulations were published in the Canada Gazette. These updates are intended to, among other things, strengthen Canada’s anti-money laundering (AML) regime and address certain technical issues. The draft does expand the definition of a money services business (MSB) to include “dealers in digital currency,” but digital currency businesses may still consider submitting comments related to the draft, as the consultation period of 60 days is open to the public.
On July 4th, 2015, draft amendments to Canada’s Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Regulations were published in the Canada Gazette. These updates are intended to, among other things, strengthen Canada’s anti-money laundering (AML) regime and address certain technical issues. The draft does expand the definition of a money services business (MSB) to include “dealers in digital currency,” but digital currency businesses may still consider submitting comments related to the draft, as the consultation period of 60 days is open to the public.
This round of amendments didn’t include ‘dealers in digital currency’ – so why should you comment?
While dealers in digital currency are not yet regulated as MSBs, it is reasonable to expect that this is the direction Canada is taking based on Bill C-31, which was passed last year. This means that the regulations could apply to digital currency businesses in the near future. The 60-day comment period is likely to be the only public comment period before a final version of the amended regulations is published.
One of the most significant changes in the current draft relates to customer identification. The current customer identification methods for non-face-to-face customers (which apply to all online MSB customers) are complicated and heavily reliant on an individual having at least six months of Canadian credit history (you can learn more here). The proposed amendments have the potential to broaden the range of available sources to include sources other than credit reporting bureaus.
Digital currency businesses should consider commenting on these amendments. While we at Outlier consider the changes to be positive overall, we’re aware that there are many identification solutions on the market (many of which don’t meet the current Canadian identification requirements). This has caused more than a few headaches for businesses that operate online. While the proposed changes may alleviate some of the current pain points, businesses should consider how these fit with your business model and service providers.
Customer Identification Measures
In the text below, the text that is struck through includes proposed deletions, while the green text includes proposed additions. You can also see a full marked-up version of the Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Regulations here.
MEASURES FOR ASCERTAINING IDENTITY
- (1) In the cases referred to in sections 53, 53.1, 54, paragraph 54.1(a) and sections 55, 56, 57, 59, 59.1, 59.2, 59.3, 59.4, 59.5, 60 and 61, a person’s the identity of a person shall is to be ascertained, at the time referred to in subsection (2) and in accordance with subsection (3), in the following manner:
(a) By referring to the person’s birth certificate, driver’s licence, provincial health insurance card (if such use of the card is not prohibited by the applicable provincial law), passport or other similar document; or
(a) By referring to identification document that contains their name and photograph and that is issued by the federal government or a provincial government or by a foreign government other than a municipal government, and by verifying that the name and photograph are those of the person;
(b) if the person is not physically present when the account is opened, the credit card application is submitted, the trust is established, the client information record is created or the transaction is conducted,
(i) by obtaining the person’s name, address and date of birth and
(A) confirming that one of the following entities has identified the person in accordance with paragraph (a), namely,
(I) an entity, referred to in any of paragraphs 5(a) to (g) of the Act, that is affiliated with the entity ascertaining the identity of the person,
(II) an entity that carries on activities outside Canada similar to the activities of a person or entity referred to in any of paragraphs 5(a) to (g) of the Act and that is affiliated with the entity ascertaining the identity of the person, or
(III) an entity that is subject to the Act and is a member of the same association as the entity ascertaining the identity of the person, and
(B) verifying that the name, address and date of birth in the record kept by that affiliated entity or that entity that is a member of the same association corresponds to the information provided in accordance with these Regulations by the person, or
(ii) subject to subsection (1.3), by using one of the following combinations of the identification methods set out in Part A of Schedule 7, namely,
(A) methods 1 and 3,
(B) methods 1 and 4,
(C) methods 1 and 5,
(D) methods 2 and 3,
(E) methods 2 and 4,
(F) methods 2 and 5,
(G) methods 3 and 4, or
(H) methods 3 and 5.
(b) by referring to information concerning them that is received by the person or entity that is ascertaining their identity on request from a federal or provincial government body — or a body that is acting as the agent or mandatary of such a body — that is authorized in Canada to ascertain the identity of persons, and by verifying that either the name and address or the name and date of birth contained in the information are those of the person;
(c) by referring to information that is contained in the person’s credit file — if that file is located in Canada and has been in existence for at least three years — and by verifying that the name, address and date of birth contained in the credit file are those of the person;
(d) by doing any two of the following:
(i) referring to information from a reliable source that contains their name and address, and verifying that the name and address are those of the person,
(ii) referring to information from a reliable source that contains their name and date of birth, and verifying that the name and date of birth are those of the person, or
(iii) referring to information that contains their name and confirms that they have a deposit account or a credit card or other loan account with a financial entity, and verifying that information; or
(e) by confirming that one of the following entities previously ascertained their identity in accordance with any of paragraphs (a) to (d), and by verifying that the name, address and date of birth contained in the entity’s record are those of the person:
(i) an entity that is referred to in any of paragraphs 5(a) to (g) of the Act and that is affiliated with the entity that is ascertaining the person’s identity,
(ii) an entity that carries on activities outside Canada similar to the activities of a person or entity referred to in any of paragraphs 5(a) to (g) of the Act and that is affiliated with the entity that is ascertaining the person’s identity, or
(iii) a financial entity that is subject to the Act and that is a member of the same financial services cooperative or credit union central as the entity that is ascertaining the person’s identity.
(1.1) In the case referred to in paragraph 54.1(a), the identity of a person shall be ascertained by a person or entity, at the time referred to in subsection (2) and in accordance with subsection (3),
(a) by referring to the person’s birth certificate, driver’s licence, provincial health insurance card (if such use of the card is not prohibited by the applicable provincial law), passport or other similar document; or
(b) where the person is not physically present when the credit card application is submitted,
(i) by obtaining the person’s name, address and date of birth and
(A) confirming that one of the following entities has identified the person in accordance with paragraph (a), namely,
(I) an entity, referred to in any of paragraphs 5(a) to (g) of the Act, that is affiliated with the entity ascertaining the identity of the person,
(II) an entity that carries on activities outside Canada similar to the activities of a person or entity referred to in any of paragraphs 5(a) to(g) of the Act and that is affiliated with the entity ascertaining the identity of the person, or
(III) an entity that is subject to the Act and is a member of the same association as the entity ascertaining the identity of the person, and
(B) verifying that the name, address and date of birth in the record kept by that affiliated entity or that entity that is a member of the same association corresponds to the information provided in accordance with these Regulations by the person,
(ii) subject to subsection (1.3), by using a combination of any two identification methods referred to in either Part A or Part B of Schedule 7, or
(iii) subject to subsection (1.3), where the person has no credit history in Canada and the credit limit on the card is not more than $1,500, by using combination of any two identification methods referred to in any of Parts A, B and C of Schedule 7.
(1.1) For the purposes of subparagraphs (1)(d)(i) to (iii), the information that is referred to must be from different sources, and the person whose identity is being ascertained and the person or entity that is ascertaining their identity cannot be a source.
(1.2) for the purposes of paragraphs (1)(b)(i) and (1.1)(b)(i), an entity is affiliated with another entity if one of them is wholly owned by the other or both are wholly owned by the same entity.
(1.2) The person or entity that is ascertaining the identity of a person who is at least 12 years of age but not more than 15 years of age may refer under subparagraph (1)(d)(i) to information that contains the name and address of one of the person’s parents or their guardian or tutor in order to verify that the address is that of the person.
(1.21) For the purposes of subparagraphs (1)(b)(i) and (1.1)(b)(i),
(a) a financial services cooperative and each of its members that is a financial entity are considered to be members of the same association; and
(b) a credit union central and each of its members that is a financial entity are considered to be members of the same association.
(1.3) A combination of methods referred to in sub-paragraph (1)(b)(ii) or (1.1)(b)(ii) or (iii) shall not be relied on by a person or entity to ascertain the identity of a person unless
(a) the information obtained in respect of that person from each of the two applicable identification methods is determined by the person or entity to be consistent; and
(b) the information referred to in paragraph (a) is determined by the person or entity to be consistent with the information in respect of that person, if any, that is contained in a record kept by the person or entity under these Regulations.
(1.3) If a document is used to ascertain identity under subsection (1), it must be original, valid and current. Other information that is used for that purpose must be valid and current and must not include an electronic image of a document.
(2) The identity shall be ascertained
(a) in the cases referred to in paragraph 54(1)(a) and subsection 57(1), and paragraph 60(a), before any transaction other than an initial deposit is carried out on an account;
(b) in the cases referred to in section 53, paragraph 54(1)(b), subsection 59(1) and paragraphs 59.3(a), 59.4(1)(a), 59.5(a), 60(b) and 61(b), at the time of the transaction;
(b.1) in the case referred to in section 53.1, before the transaction is reported as required under section 7 of the Act;
(b.2) in the case referred to in paragraph 54.1 (a), before any credit card is activated;
(c) in the cases referred to in paragraphs 55(a), (d) and (e), within 15 days after the trust company becomes the trustee;
(d) in the cases referred to in subsection 56(1) and paragraph 61(a), within 30 days after the client information record is created;
(e) in the cases referred to in paragraphs 59.1(a) and 59.2(1)(a), at the time of the transaction; and
(e.1) in the case referred to in paragraph 60(a), before any funds are disbursed; and
(f) in the case referred to in subsection 62(3), at the time a contribution in respect of an individual member of the group plan is made to the plan, if
(i) the member’s contribution is not made as described in paragraph 62(3)(a), or
(ii) the existence of the plan sponsor has not been confirmed in accordance with section 65 or 66.
(3) Unless otherwise specified in these Regulations, only original documents that are valid and have not expired may be referred to for the purpose of ascertaining identity in accordance with paragraph (1)(a) or (1.1)(a).
64.1 (1) A person or entity that is required to take measures to ascertain a person’s identity under subsection 64(1) or (1.1) may rely on an agent or mandatary to take the identification those measures described in that subsection only if that person or entity has entered into an agreement or arrangement, in writing, with that agent or mandatary for the purposes of ascertaining identity.
(2) A person or entity that enters into an agreement or arrangement referred to in subsection (1) must obtain from the agent or mandatary the customer information obtained by the agent or mandatary under that agreement or arrangement.
(2) The person or entity may rely on measures that were previously taken by an agent or mandatary to ascertain the person’s identity if the agent or mandatary was, at the time they took the measures,
(a) acting in their own capacity, whether or not they were required to take the measures under these Regulations; or
(b) acting as an agent or mandatary under a written agreement or arrangement — entered into with another person or entity that is required to take measures to ascertain a person’s identity — for the purposes of ascertaining identity under subsection 64(1).
(3) In order to rely on measures taken by an agent or mandatary under subsection (1) or (2), the person or entity shall
(a) have entered into a written agreement or arrangement with the agent or mandatary for the purposes of ascertaining a person’s identity under subsection 64(1);
(b) obtain from the agent or mandatary all of the information that the agent or mandatary used to ascertain the person’s identity; and
(c) be satisfied that the information is valid and current and that the agent or mandatary ascertained the person’s identity in the manner described in any of paragraphs 64(1)(a) to (d).
64.2 Every person or entity that is required under these Regulations to ascertain a person’s identity in connection with a record that the person or entity has created and is required to keep under these Regulations — or in connection with a transaction that they have carried out and in respect of which they are required to keep a record under these Regulations or under section 12.1 of the Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Suspicious Transaction Reporting Regulations — shall set out on or in, or include with, that record the person’s name and the following information:
(a) if the person or entity referred to an identification document under paragraph 64(1)(a), the type of document referred to, its reference number and the issuing authority and, if available, the place it was issued and its expiry date;
(b) if the person or entity referred to information under paragraph 64(1)(b), the source of the information, the type of information referred to, a reference number associated with the information and the date on which the person or entity verified the information;
(c) if the person or entity referred to information under paragraph 64(1)(c), the source of the information, the reference number associated with the search of the credit file and the date on which the person or entity verified the information;
(d) if the person or entity referred to information under paragraph 64(1)(d), the source of the information, the type of information referred to and the account number contained in it — or if there is no account number contained in it, a reference number associated with the information — and the date on which the person or entity verified the information; or
(e) if the person or entity confirmed under paragraph 64(1)(e) that another entity had previously ascertained the person’s identity, the name of that entity, the manner in which it previously ascertained the person’s identity under any of paragraphs 64(1)(a) to (d), the applicable information set out in one of paragraphs (a) to (d) of this section that is associated with that manner of ascertaining identity and the date on which the person or entity verified the information.
Submit comments by September 12, 2015
Comments must be submitted in writing during the comment period, either by email or snail mail:
Snail Mail:
Lisa Pezzack, Director Financial Systems Division,
Financial Sector Policy Branch Department of Finance
90 Elgin Street Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0G5
Email:
fcs-scf@fin.gc.ca
Need a Hand?
At Outlier, we believe that it is important to participate in decisions that affect you and your business. If you would like someone to look over your submission before you make comments to the Department of Finance, you can get in touch with us free of charge. We will look over your submission and make suggestions, without any cost to you. If you need a hand, please feel free to contact us.














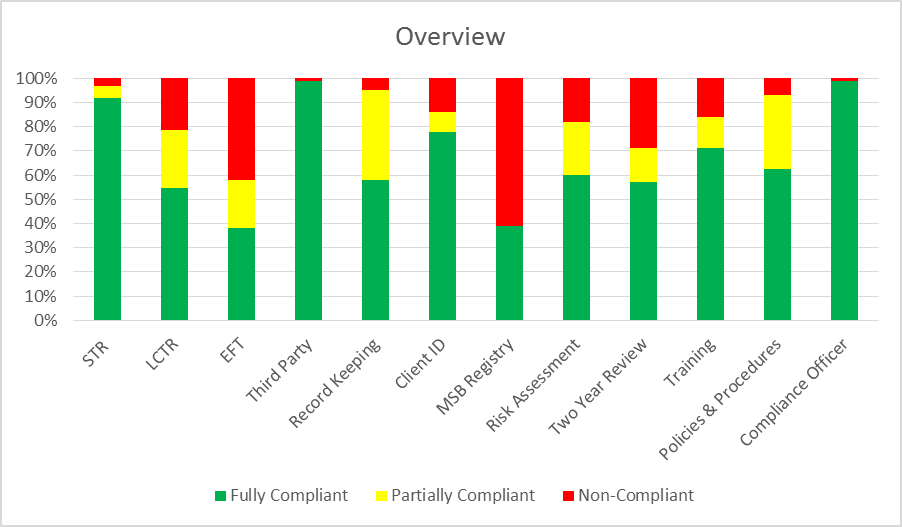

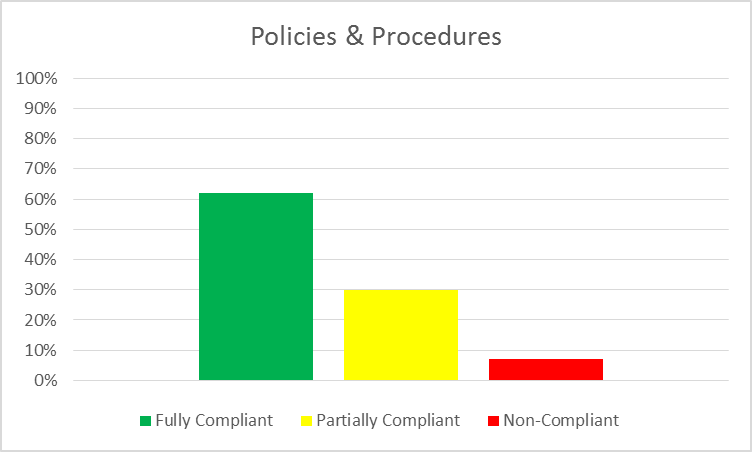





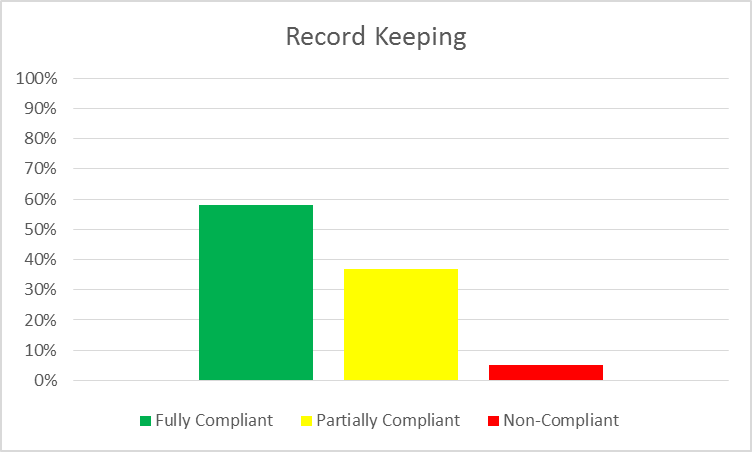




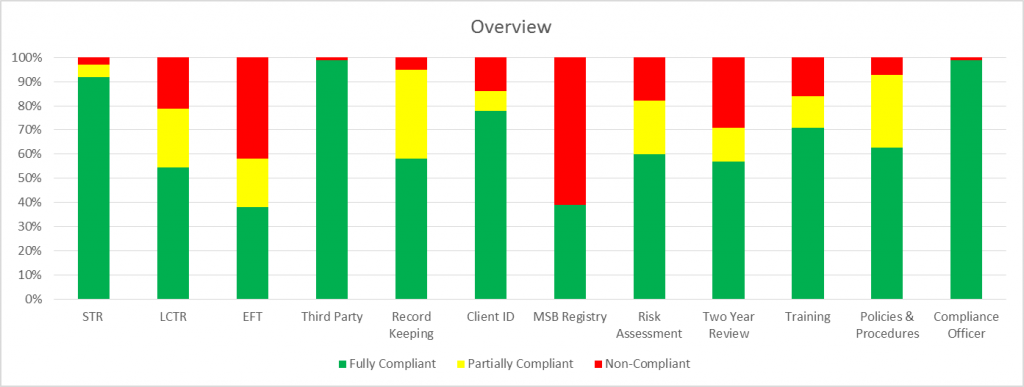


Proposed AML Amendments & Credit Unions
Background
On July 4, 2015, draft amendments to the Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Regulations (PCMLTFR) were published in the Canada Gazette. These changes are not yet in force, and are open to public comment until September 4, 2015. The proposed changes are based on requirements set out by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an inter-governmental body that sets out international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing. For this reason, we expect the final version of these amendments to be similar to the draft text.
2015 Proposed PCMLTFR Amendments and Credit Union Specific Analysis (Line By Line)
Why Do These Changes Matter to Credit Unions?
The proposed changes will have a direct impact on a Credit Union’s AML obligations, including record keeping, member identification and ongoing monitoring requirements. Some of the more significant changes include new member identification methods, expanded definitions (and requirements) for Politically Exposed Persons, and new record keeping requirements for “reasonable measures” taken.
New Member Identification Methods
The amendments also provide a number of new identification methods that can be used to identify members both face-to-face and non-face to face. These new methods are an improvement on existing rules, which are currently more restrictive.
For example, a Canadian credit file meeting certain criteria could now be used to identify a member. Many credit unions perform credit checks as part of their account opening process, so this could be used in place of government-issued identification in certain circumstances, or would allow simple non-face to face identification.
Also added is the ability to rely on information from “a reliable source” (yet to be determined, but likely online databases and other web-based resources), and information confirming that an individual has a deposit account, credit card or other loan account with another credit union, bank or caisse populaire. A credit union will also be able to accept identification performed by another credit union.
Politically Exposed Persons
Given that the list (contained in bill C-31) of qualifying positions for PEDPs includes mayors, it is likely that many if not most credit unions will have members classified as PEDPs. The draft regulations mitigate this somewhat by adding a prescribed period of 20 years to the definition of a PEDP.
Additionally, required measures for PEPs such as determining the source of funds, obtaining senior management authorization to keep an account open, and performing enhanced monitoring will only apply to PEDPs and HIOs (and their family members and close associates) who have been determined to be high risk. Despite these exceptions, identifying and documenting these new categories of PEP will add to credit unions’ compliance obligations.
Reasonable Measures
Many AML record keeping, reporting and determination requirements rely on “reasonable measures” to be taken by financial institutions. For example, in a Large Cash Transaction Report, certain information about the conductor of the transaction, such as their country of residence, their home and business telephone numbers are not mandatory, but reasonable efforts must be made to obtain the information, and if you have it on file, it must be included in the report. The proposed changes will mean that whenever you take “reasonable measures”, and the measures taken are unsuccessful, you will then need to keep a record describing what the measures were and the reason they were unsuccessful. This will require additional work and record keeping for categories such as FINTRAC reporting, PEP determinations and correspondent banking relationships, among others.
Public Comments
Public comments about the proposed changes will be accepted by the Ministry of Finance until September 4, 2015. They must be submitted in writing, as follows:
Mail Attention: Lisa Pezzack
Director, Financial Systems Division
Department of Finance
90 Elgin Street
Ottawa, Ontario, K1A 0G5
Email: fcs-scf@fin.gc.ca
Need a Hand?
If you would like someone to look over your submission before you make comments to the Department of Finance, you can get in touch with us free of charge. We will look over your submission and make suggestions, without any cost to you. If you need a hand, please feel free to contact vCAMLO or Outlier.