The Canadian Money Services Business Association (CMSBA) recently held their Spring Training events in Montreal, Vancouver and Toronto. The list of speakers included MSB industry professionals, as well as representatives from regulators including the Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC). For a full synopsis of the Montreal and Toronto events, click here. FINTRAC presented excellent statistical data about how MSBs have fared in examinations conducted between April 2011 and July 2014. So how are MSBs faring? Very well overall.

Data obtained through a freedom of information request indicates that almost 25% of MSBs examined between 2008 and 2013 have not had any deficiencies.
How Does FINTRAC Decide Who Is Examined?
FINTRAC considers several factors when deciding which reporting entities (REs) will be examined.
- Concurrent Examinations: examinations conducted in tandem with the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI). This is applicable to federally regulated financial entities (FRFEs) like banks.
- Market Share: The largest reporting entities in Canada (because the larger an organization is, the more critical the risk of non-compliance will be);
- Cyclical: Coverage of a whole industry (this seemed to apply most to Casinos).
- Follow-Up: Subsequent examinations based, with an emphasis on the resolution of deficiencies found in previous examination(s) to ensure remediation. FINTRAC noted that although it is no longer a requirement to submit a formal action plan to FINTRAC, it is a best practice for REs to document (and update) an action plan internally.
- Risk: FINTRAC’s evaluation of the RE’s risk, based on a broad selection criteria, such as money laundering and terrorist financing vulnerabilities, the likelihood of non-compliance and industry trends.
- Theme-Based: Related to specific intelligence about a RE or type of business that indicates there may be an elevated risk of non-compliance, money laundering vulnerability or terrorist financing vulnerability.
Methodology & Analysis
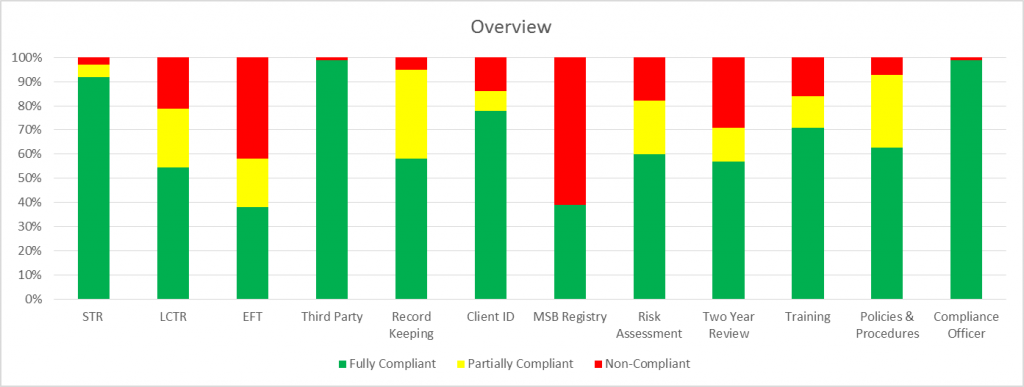
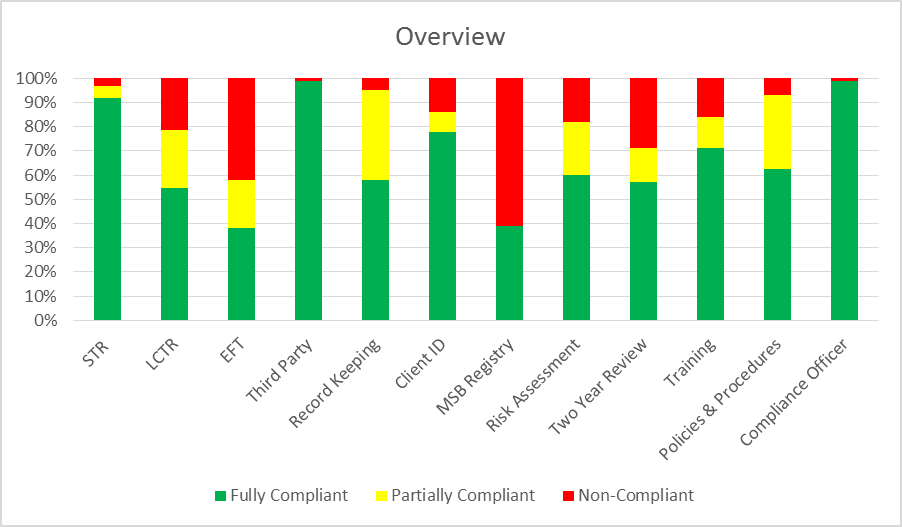
FINTRAC’s statistical analysis of MSB adherence to the requirements laid out in the Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act (PCMLTFA) and its regulations is broken down by percentage, the results of the exams conducted that were fully compliant, partially compliant and non-compliant. These are colour coded:
- Green: fully compliant (no deficiencies were observed),
- Yellow: partially compliant (there was something in place, but the MSB missed something), and
- Red: non-compliant (in most cases, there was nothing in place or a reporting timeframe was missed).
Overall examination results have been positive.
It’s noteworthy that if FINTRAC has, as of 2014, found something during an examination that is considered ‘immaterial’, it’s not cited. For example, in a large sample, if there are two client addresses that appear to be PO boxes, but all other client addresses were complete and in acceptable formats, there may not be a citation. In these cases, FINTRAC may inform the RE verbally, but it will not be part of the formal ‘findings’ letter.
Compliance Officer
MSBs are required to have a Compliance Officer (a person that is responsible for overseeing the AML & ATF compliance program). The appointment of the Compliance Officer must be documented in writing. FINTRAC staff chided that this is likely the easiest area to achieve a fully compliant result in examinations. MSB examination results certainly reflected this.

From a total of 612 MSB examinations considered, 608 MSBs were fully compliant.
Only four MSBs were deemed to be non-compliant. It was noted that these were generally new market entrants that did not appear to understand Canadian AML & ATF compliance requirements.
Policies and Procedures
MSBs are required to have policies and procedures. Policies describe the MSB’s regulatory obligations, while procedures describe what the MSB is doing to meet those requirements. These must be documented, in writing, and the procedures must cover both staff and agents (if the MSB has agents).
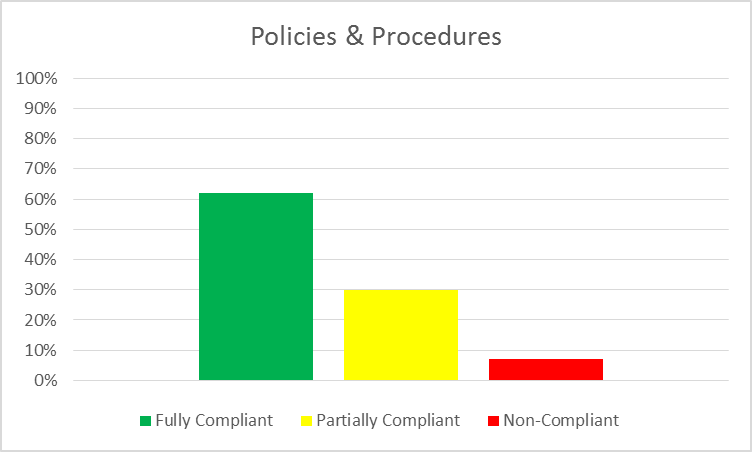
From a total of 765 MSB examinations considered, 477 MSBs were fully compliant.
In 230 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. Common errors included:
- The omission of the 24-hour rule (specific descriptions of how the MSB determined whether or not reportable transactions had occurred over a 24 hour period),
- Third party determinations (specific descriptions of when an MSB must determine if there is a third party involved, as well as what information needs to be collected and recorded), and
- Politically exposed foreign person (PEFP) determinations (specific descriptions of when an MSB must determine if their client is a PEFP, and if so, what information needs to be collected/recorded. There is also a requirement that senior management signoff on the account within 30 days of the determination).
A total of 55 MSBs did not have any documented policies or procedures. In some cases, FINTRAC noted that there appeared to be processes in place, but that these were not documented in writing.
Training
MSBs are required to have an ongoing training program. The training program must be documented (who, what, where, when and how) and delivered to all staff and agents on an annual basis, at minimum.

From a total of 487 MSB examinations considered, 346 were fully compliant.
In 63 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. Common errors included:
- Interviews conducted with staff during an examination that evidenced a misunderstanding of the requirements (during an exam, FINTRAC will interview random staff members related to regulatory requirements to ensure training effectiveness)
In 78 examinations, MSBs did not have any training in place, or if they did, it was not documented.
Among the training options available to MSBs, we’re most excited about a relatively new offering from TAMLO that includes fast paced and visually stunning video content, as well as testing and tracking tools for Compliance Officers.
AML Compliance Effectiveness Review
MSBs are required to complete an AML Compliance Effectiveness Review once every two years. The review must cover all policy and procedure documentation, as well as operational testing to ensure procedures are being properly followed.

From a total of 722 MSB examinations considered, 412 were fully compliant.
In 101 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. Where MSBs missed the mark was typically because they did not respect the two year cycle. Other common errors included:
- Only reviewing the policy documents with no operational testing of whether they are being followed (the policy document tells staff and agents what to do. Procedures tell them how to do it. MSBs must be sure they are testing whether staff and agents are adhering to the procedures).
In 209 examinations, MSBs had not conducted an effectiveness review or could not provide evidence of one taking place.
Risk Assessment
MSBs are required to assess the risk that their business could be used for money laundering or terrorist financing. The risk assessment must include four key components:
- Products, services and delivery channels;
- Geography;
- Customers; and
- Any other relevant factors.
Risk must be assessed and scored, and mitigated by appropriate controls.

From a total of 720 MSB examinations considered, 432 were fully compliant.
In 158 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. The main issue was failing to include one of the four required elements. In some cases, a risk assessment was in place, but the documentation was not sufficient in assessing the MSB’s risk and controls.
In 129 examinations, MSBs had no evidence of a risk assessment.
FINTRAC noted that additional industry-specific risk assessment guidance is expected to be published later this year.
MSB Registration
MSBs are required to register with FINTRAC, as well as update their information within 30 days if there are any changes to business activities, banking or agent information.

From a total of 591 MSB examinations considered, 230 were fully compliant.
In this category, no partially compliant ratings were provided (the MSB registration was either complete, accurate and up to date, or it was deemed to be non-compliant).
In 361 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be non-compliant. Most issues were due to a failure to update information when something within the business had changed or a failure to list all business activities. For example, the MSB registration may indicate that an MSB only performed foreign exchange in a case where remittance services were also provided.
Client Identification
MSBs are required to identify their clients in certain situations. There are prescribed methods for completing this both in person and non-face-to-face (NF2F), and the identification document (ID) information must be recorded.

From a total of 796 MSB examinations considered, 621 were fully compliant.
In 64 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. Common errors included:
- Unacceptable ID (such as health card in Ontario);
- Accepting ID that was expired at the time of the transaction (identification documents must be valid, or not expired, at the time they are reviewed);
- Failing to record the prescribed details of the ID used (when reviewing a client’s ID, MSBs must keep a record of certain prescribed information); and
- In Non-Face-To-Face Identification situations, only using one method, or using an unacceptable combination of methods (when identifying a customer who is not physically present, there are prescribed methods of how this is to be accomplished).
In 111 examinations, MSBs were non-compliant with client identification requirements.
Record Keeping
MSBs are required to keep certain records related to transactions and client identification. These records must be stored in a manner that they can be accessed in the event they are requested, and must be maintained for at least five years.
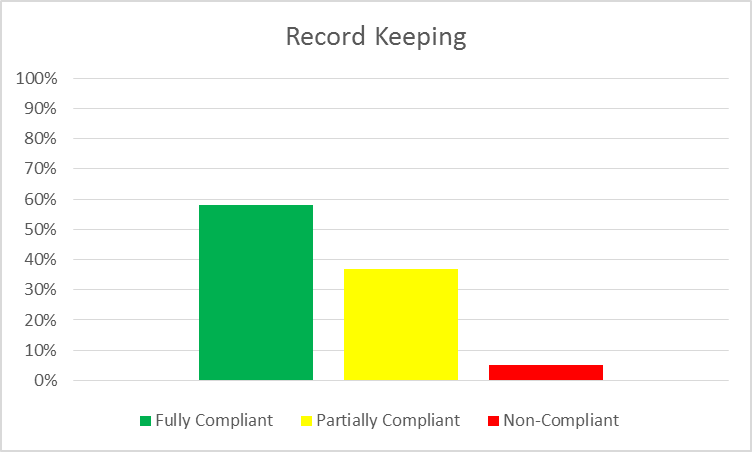
From a total of 811 MSB examinations considered, 470 were fully compliant.
In 300 examinations MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. In these cases, record keeping was taking place but elements of the record keeping requirements were being overlooked. Common issues included:
- Missing telephone numbers;
- Vague occupation information (for example “manager” or “worker”);
- PO boxes recorded as customer addresses;
- Missing postal codes;
- Third party determinations that were incomplete; and
- Payment methods for incoming and outgoing payments.
In 41 examinations, MSBs were non-compliant with record keeping requirements.
Third Party Determinations
MSBs are required to make a third party determination in certain prescribed circumstances, as well as collect and record certain information (name, address, date of birth, occupation and relationship to your client) about the third party.

The total number of MSBs included in the review was not provided, with the statement: “there was not enough information available to conduct reasonable analysis”. However, the total number of non-compliant MSBs was 6, indicating that approximately 600 MSB examinations were considered in this sample.
FINTRAC Reporting
When FINTRAC assesses reporting obligations, it uses the internal acronym “QTV”, which stands for quality, timing and volume. Quality refers to the information in the report, specifically, if the report has all the required information. Timing simply means, was the report filed within the designated timeframe. Volume is slightly more complicated, but mainly refers to the amount of reports you have filed compared to your previous submissions. It was noted that typically, where MSBs were deemed partially compliant, it was due to the quality. Where non-compliance was related to the timing.
Electronic Fund Transfers Reports
MSBs are required to submit electronic funds transfer (EFT) reports to FINTRAC within 5 business days from the date the transaction took place. An EFT includes the international transfer of CAD 10,000 or more, either in a single transaction, or multiple transactions within a 24-hour period.

From a total of 434 MSB examinations considered, 165 were fully compliant.
In 87 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. MSBs were typically failing to include all required information, such as:
- Phone number;
- Date of birth; or
- Postal code.
It is noteworthy that while not all fields are marked as required in F2R, all fields must be filled in if the MSB has recorded the information.
In 182 examinations, MSBs were deemed non-compliant, with most not reporting the EFTs within the specified time frame, and a small portion missing EFT reports.
Large Cash Transaction Reports
MSBs are required to submit large cash transaction (LCT) reports to FINTRAC within 15 calendar days from the date of the transaction, if the transaction was CAD 10,000 or more in cash, either in a single transaction, or multiple transactions within a 24-hour period.

From a total of 428 MSB examinations considered, 232 were fully compliant.
In 104 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. MSBs were typically failing to include all required information, such as:
- Occupation;
- Date of birth;
- Postal code; or
- Type of ID used to identify the client.
In 92 examinations, MSBs were non-compliant, with most not reporting the LCTs within the specified time frame, and a small portion missing LCT reports.
Suspicious Transaction Reports
MSBs are required to submit suspicious transaction reports (STRs) and attempted suspicious transaction reports (ASTRs) to FINTRAC within 30 calendar days from the date the transaction is deemed suspicious by the Compliance Officer.

From a total of 285 MSB examinations considered, 262 were fully compliant.
In 14 examinations, MSBs were deemed to be partially compliant. In these cases, MSBs were typically failing to include all required information.
In 9 examinations, MSBs were non-compliant. Failing to file STRs carries relatively sever penalties, as the Canadian intelligence community relies on this type of reporting to build cases. Where items are escalated as being potentially suspicious (either by staff or a transaction monitoring system), MSBs should always document the reason that these items are deemed not to be suspicious if no STR or ASTR reporting is completed.
Need a Hand?
If you are an MSB that needs compliance assistance (or a bank that wants assistance in setting up and maintaining a compliance regime that effectively manages MSB related risk), please contact us.
 OSFI
OSFI